
[tabs]
[tab title=”Project”]
The project “Photonic biosensing for monitoring biological activities of bacteria and selected eukaryotic cells immobilized on biofunctionalized surfaces of quantum semiconductors” represents a new direction of research in the QS-PBNT Laboratory aimed at monitoring biological activity of live bacteria and selected eukaryotic cells immobilized on biofunctionalized surfaces of QS microstructures. The idea is to collect photoluminescence (PL) maps of QS microstructures interfaced with live biological cells for studying the reaction of cells exposed to different environments. From the information about spatially resolved PL intensity signal, one could deduce the distribution of electric charge on the cell surface. Electrical potentials associated with cell membranes are involved in a large number of cellular processes, thus, being able to measure such potentials makes it possible to study these processes and the functioning of cells in different environments. Photonic measurements of electric charge induced effects in biological cells have the advantage of “non-contact” rapid diagnostics. Our approach is to take advantage of this property and demonstrate monitoring of some cellular functions that until now were either impossible to observe, or required the application of complicated (expensive) tools. The results of this project have the potential to lead to significant progress in biological cell study, advancement of methods for therapeutic cell treatment and drug discovery.
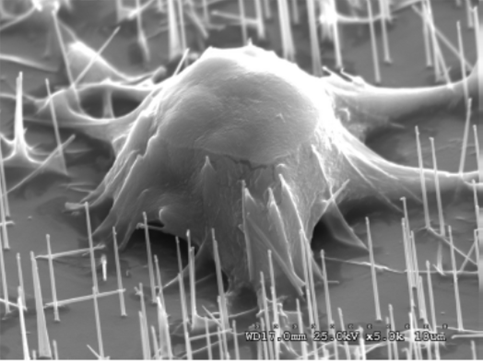
SEM image of a mouse embryonic stem (mES) cell interfaced with silicon nanowires [Kim et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129, 7228-7229 (2007)].
[/tab]
[tab title=”Curriculum”]
- February 2008
Ranked 7 among 1000 students in the entrance exam to Azad universities of Iran for the M.Sc program in Biomedical Engineering. - Ranked 420 among 3000 students in the entrance exam to state universities of Iran for the M.Sc program in Telecommunication Engineering, and 580 among the same number of students in the entrance exam to state universities of Iran in Biomedical Engineering.
- July 2003
Ranked 505 among 400000 participants in the entrance exam to states universities of Iran for the B.Sc program - 1996- 2003
Student in Farzanegan school which is a division of NODET (National Organization for Developing Exceptional Talents) in Kermanshah, Iran.
- 2012 –
PhD Electrical Engineering – Biophotonics
University of Sherbrooke, Canada - 2008 – 2011
MSc Electrical Engineering – Telecommunication Engineering
K.N. Toosi University of Technology, Tehran, Iran. - 2003 – 2008
BSc Biomedical Engineering
Amirkabir University of Technology, Tehran, Iran
- January 2010-July 2010
Research Assistant
K. N. Toosi University of Technology, Tehran, Iran - July 2008-March 2010
Assistant Project Manager
Isis Innovation Ltd, England - 2003 – 2004
Observer Engineer
Tehran, Iran - May 2006-September 2006
Intern
Shahid Beheshti University (Medicine Department), Tehran, Iran
[/tab]
[tab title=”Publications”]
- E. Nazemi and N. Granpayeh, “Ultra Compact Plasmonic Bandpass Filter”, published in the Nanometa 2011 (the 3rd international topical meeting on Nanophotonics and Metamaterials Symposium in Seefeld ski resort, Tirol, Austria), Europhysics Conference Abstract Volume 35A, ISBN No2-914771-65-7.
- E. Nazemi and N. Granpayeh, “Simulation of a plasmonic gas sensor used for detection of gaseous particles and their refractive index in environment”, published in the Nanometa 2011 (the 3rd international topical meeting on Nanophotonics and Metamaterials Symposium in Seefeld ski resort, Tirol, Austria), Europhysics Conference Abstract Volume 35A, ISBN No2-914771-65-7.
[/tab]
[tab title=”Contact”]
Elnaz Nazemi
Université de Sherbrooke
Interdisciplinary Institute for Technological Innovation (3IT)
3000, boul. de l’Université
Sherbrooke, Québec
J1K 0A5, CANADA
Office: 4000.9
Email: [email protected]
Phone: +1-819-821-8000 ext. 65724
Fax: +1-819-821-7937
[/tab]
[/tabs]

